
Although most people use the Tor browser to access the dark web, it can also be used free of charge to gain privacy while surfing the normal indexed web (clear web/surface web). The benefit of using Tor to surf the regular internet is that your activities will be private. Thanks to a strong layer of encryption, your ISP cannot know which websites you’re visiting.
Staying Safe Online
The deep and dark web is a treasure-trove of information on threat actor activity, however making use of this resource to protect your organization can be (to the uninitiated), challenging. As a rule, this side of the internet hides content, identities, and locations from third parties that are common throughout the ‘surface web’ (mainstream, public websites). In Tor’s case, this is facilitated by routing encrypted traffic through layers of relays around the world. In addition, NordVPN servers wipe data on every reboot because they are RAM-based. If a law enforcement agency seizes or infiltrates a server to investigate a user’s dark web activity, they will find no data or Tor browsing history.
Similarities And Differences
Each layer of the internet requires users to approach their activities with mindfulness, adopting necessary precautions to protect themselves against potential threats. In an increasingly digital world, the internet has become an essential element of our daily lives. We rely on it for communication, shopping, learning, and entertainment. Yet, the surface internet we routinely access is only a fraction of what the web truly encompasses. Beneath the familiar websites lie layers of content that most users know little about. Among these layers, the terms “Deep Web” and “Dark Web” often surface in discussions about internet safety and privacy.
How Do You Access The Dark Web?
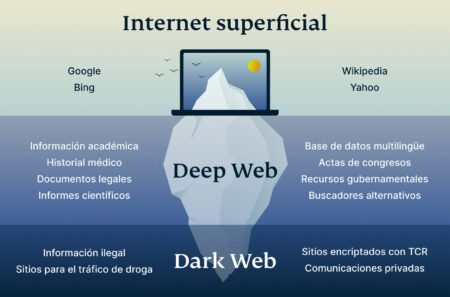
Though they’re often used interchangeably to refer to the more questionable areas of the internet, they’re quite different. And understanding these differences is a dive into the true depth of the internet. While the average person usually limits their browsing to the “surface web,” these other parts of cyberspace re still teeming with life and have become home to many users, both benign and nefarious. With that said, here’s all you need to know about the dark web, the deep web, and their differences. The Deep Web hosts everything behind a login or paywall—email, personal data, cloud data, medical records, etc.
- The Deep Web thus balances safeguarding data with the practicalities of access, a dynamic critical to modern digital operations.
- The dark web was originally a domain exclusively used by cybercriminals and governments.
- Plus, it features a built-in VPN to encrypt your connection, hiding your IP address and online activity, for more anonymous and private browsing.
- Additionally, the technology for onion routing was actually developed by the U.S.
- The anonymity provided by the dark web does indeed make it ideal for people looking to engage in illicit activity.
However, illegally accessing deep web content and services, such as hacking into an account, is a criminal offense. Deep Web sites and services are easily accessible via web browsers like Google Chrome, Firefox and Microsoft Edge. The difference from surface websites is that most deep websites require users to pay for a subscription or create an online profile to obtain login credentials. Even free online services that are open to the public can be categorized as part of the deep web.
The Internet Is Not The Web
The critical thing to remember is that accessing the dark web can be dangerous if you don’t know what you’re doing. Surfing the dark web could cause you to access dangerous websites or illegal content. However, while the internet includes a lot of data we don’t usually see (deep web), the dark web has a reputation for concealing and facilitating criminal activities. While both the dark and deep web represent parts of the internet that fall outside the scope of traditional search engines, they differ in accessibility, use cases, and the types of threats they expose. Unlike the dark web, you don’t need any special software to access the deep web and can use your usual browser. It may, however, require a username or password for authentication.
The 5 Critical Differences

The unfortunate disadvantage is that the obscurity itself is illusory, and growing more so everyday, giving those who depend on it a false sense of security about their assets. Authentication is much better at preventing unauthorized access to resources. However, depending on the systems and software involved, authentication can be very complex to implement, and errors in implementation can undermine the purpose entirely. Consequently, using Tor (to visit the dark web) is something an average internet user does not do. And if you’re on that path, you better have reasonable explanations if it comes to that rare encounter with law enforcement. It’s important to note that Tor runs fine on its own, and by using a VPN additionally, we are just adding another layer of security and hiding the very fact that you’re using Tor.
Is The Deep Web Or Dark Web Safe To Access?
To access content on the deep web, you simply need the correct links and credentials, while the dark web requires specialized tools, like Tor. At the very bottom of the deep web is a small corner of the internet called the dark web. As threatening as it may seem, it only makes up a tiny portion of the deep web — less than 0.01%. Like the deep web, websites on the dark web aren’t indexed, so they can’t be opened using regular search engines. What makes the dark web different is that it can’t be accessed with your everyday web browser — this anonymous and decentralized portion of the internet requires a special browser.
Is It Safe To Browse The Deep Web?

In this post, we’re going to narrow down the differences between all of them and will try to picture how they are different from each other. We can clearly say that the Internet is very vast and what we use on a daily basis is only a chunk of it. The Internet is much more than that but first, one should be clear about the difference between the Internet and the Web.
Threat Intelligence Platforms
Below are strategies and tools you can use to safeguard your privacy, minimize risks, and protect your personal data in an increasingly complex digital world. Pages on the Deep Web are commonly protected by a login page, password, paywall, or other means of limiting access, and are designed to be private. Deep Web pages include personal pages like webmail inboxes and account pages on various sites. They also include internal company data and sites that are accessible via the Internet but protected by authentication.
You need the proper credentials to get in; even web crawlers are blocked from taking a peek. With only about 4 percent of all online content freely accessible (making up the surface web), the remainder is tucked away in the deep web. This means there is no easy, direct way for the general public to search this vast amount of unindexed content. In some cases, websites use various methods to block spiders and prevent indexing.
The web pages on the deep web are protected by credentials, paywalls, and are intentionally made private. However, these websites can still be accessed using common web browsers like Chrome or Firefox by knowing the URL of the page and the necessary credentials. Content that resides on the surface web is accessible because software robots called “spiders” or “crawlers” capture and index it, and search engines assign it rankings. These systems typically scan websites that contain .com, .org., .net, or a similar domain as well as some data and posts at social media sites. As these spiders capture Web pages, they follow embedded links to uncover additional content.



